Are you curious about taking creatine but not sure where to start? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! In this article, we’ll walk you through the basics of taking creatine as a beginner. By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of what creatine is, how it works, and how to incorporate it into your fitness routine. So, let’s get started!
First things first, what exactly is creatine? Creatine is a natural compound found in our muscles that helps provide energy for high-intensity activities like weightlifting or sprinting. It acts as a fuel source for our muscles, allowing us to push harder and perform better during workouts.
Taking creatine as a supplement can further enhance its benefits, leading to increased muscle strength, power, and overall performance. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll cover topics such as the different forms of creatine, recommended dosage, timing, and potential side effects. So, if you’re ready to take your fitness game to the next level, keep reading to learn more about taking creatine!
In conclusion, whether you’re just starting your fitness journey or a seasoned athlete looking for an extra edge, creatine can be a valuable tool in your arsenal. It’s important to note that while creatine is generally safe for most people, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement.
In our comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deeper into the world of creatine and provide you with all the information you need to make an informed decision. So, if you’re ready to take the plunge and explore the benefits of creatine, stay tuned for our upcoming article! Creatine for Beginners: How to Take It
What is Creatine
Understanding the concept of creatine
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in small amounts in foods like meat and fish. It is also produced by your body in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. Creatine is stored in the muscles and serves as an energy source during high-intensity exercises.
How creatine affects the body
When you perform high-intensity activities like weightlifting or sprinting, your muscles require a rapid supply of energy. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the primary energy source for muscle contractions, but its stores are limited. Creatine phosphate, which is found in your muscles, can quickly replenish ATP levels, allowing you to perform at a high intensity for short bursts.
Types of creatine supplements
There are several different types of creatine supplements available on the market. The most common form is creatine monohydrate, which is affordable, effective, and well-researched. Other types include creatine hydrochloride, creatine ethyl ester, and buffered creatine. However, creatine monohydrate remains the most popular choice among athletes and fitness enthusiasts due to its proven efficacy.
Benefits of Taking Creatine
Improved strength and power
One of the primary benefits of taking creatine is its ability to enhance strength and power output. Studies have shown that creatine supplementation can lead to increases in muscle strength, allowing you to lift heavier weights and push through plateaus. This increase in strength can translate into improved athletic performance and better overall fitness.
Increased muscle mass
Creatine has also been shown to promote muscle growth by increasing protein synthesis and reducing muscle breakdown. It helps facilitate the production of myosin, a protein essential for muscle contractions and growth. By supplementing with creatine, you can potentially experience greater gains in muscle size and improved body composition.
Enhanced athletic performance
The quick energy supply provided by creatine can have a significant impact on your athletic performance. It is particularly beneficial for sports or activities that require short bursts of intense effort, such as sprinting or weightlifting. Creatine supplementation has been shown to improve power output, speed, and overall athletic performance.

Choosing the Right Creatine Supplement
Considerations when buying creatine
When selecting a creatine supplement, there are a few factors to consider. Look for products that have undergone third-party testing to ensure their quality and purity. Additionally, consider the form of the supplement – powder, capsule, or liquid – and choose one that suits your preferences and ease of consumption.
Different forms of creatine supplements
As mentioned previously, creatine monohydrate is the most commonly used and researched form of creatine. It is also the most cost-effective. However, if you have digestive issues or prefer a different form, other options like creatine hydrochloride or buffered creatine may be worth exploring. Keep in mind that these alternative forms may have limited research supporting their efficacy.
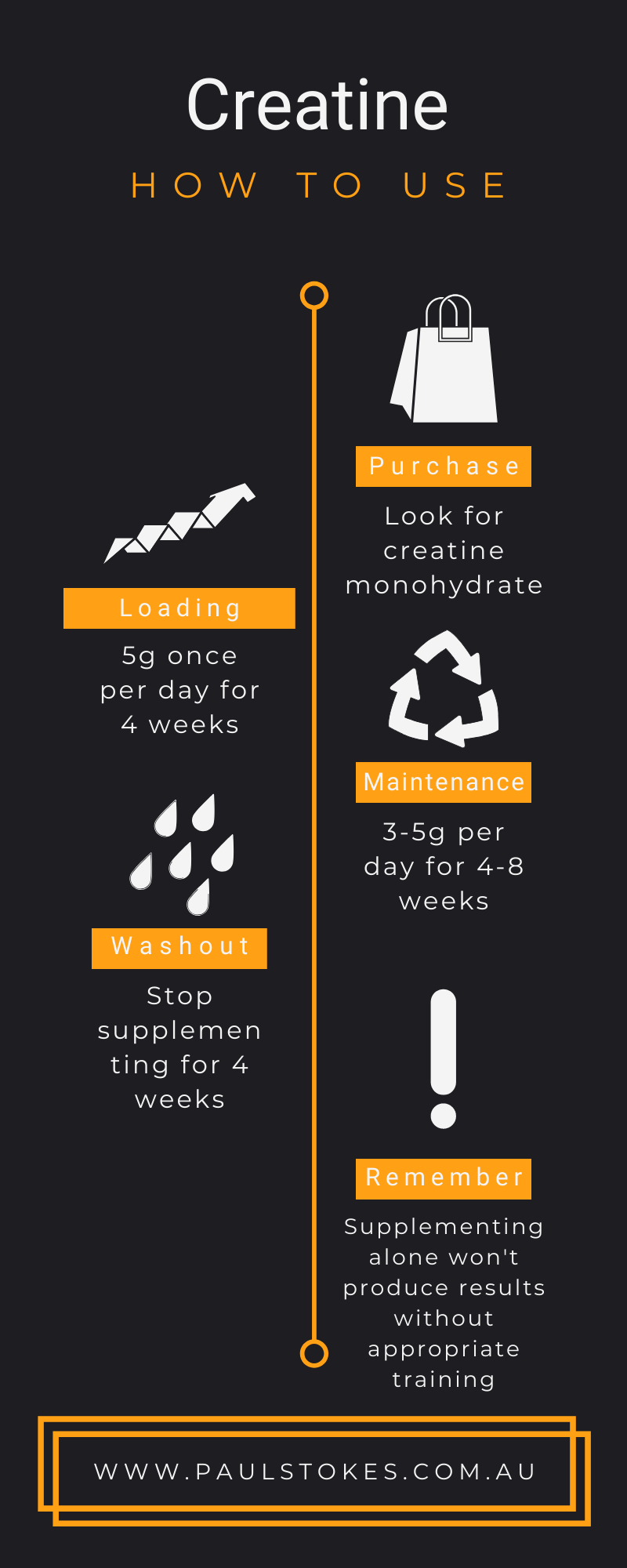
Dosage recommendations
The typical recommended dosage of creatine is around 3 to 5 grams per day. It is generally recommended to split this dosage into smaller servings throughout the day. For example, you may take 1 gram of creatine with each meal and another gram before or after your workout. However, always follow the specific instructions provided with your chosen creatine supplement, as dosages may vary.
How to Take Creatine
Loading phase vs maintenance phase
There are two common approaches to creatine supplementation: the loading phase and the maintenance phase. The loading phase involves taking a higher dose of creatine (around 20 grams per day) for the first week to saturate your muscles’ creatine stores. After the loading phase, you can switch to the maintenance phase, which involves taking a lower dose (3 to 5 grams per day) to maintain optimal creatine levels.
Proper timing for creatine consumption
Timing is not critical when it comes to taking creatine. You can take it at any time of the day that is convenient for you. Some people prefer to take it before or after their workouts, while others choose to take it with a meal. The most important factor is consistency – taking your daily dose of creatine consistently will help maintain optimal levels in your muscles.
Mixing and consuming creatine
Creatine can be easily mixed with a beverage of your choice, such as water, juice, or a protein shake. Simply add the recommended dosage of creatine to your chosen beverage and stir until it is dissolved. Drinking it immediately after mixing will ensure that you receive the full benefits of the supplement.

Possible Side Effects
Common side effects of creatine
Creatine is generally safe for most people when taken within the recommended dosage. However, some individuals may experience minor side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort, bloating, or muscle cramps. Staying properly hydrated can minimize these side effects. If you experience any severe or persistent side effects, consult your healthcare professional.
Who should avoid taking creatine
While creatine is safe for most people, there are certain populations who should avoid taking it without consulting a healthcare professional. These include individuals with pre-existing kidney or liver conditions, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and those under the age of 18. It is always best to seek medical advice if you have any concerns or specific health conditions.
Long-term effects and safety
Long-term use of creatine has not been shown to have any detrimental effects on kidney or liver function in healthy individuals. Research has indicated that creatine supplementation is generally safe when taken as directed. However, as with any dietary supplement, it is essential to follow dosage guidelines and monitor your response to ensure continued safety.
Combining Creatine with Other Supplements
Recommended supplements to stack with creatine
Creatine can be effectively combined with other supplements to enhance its benefits. Protein powders, such as whey or casein, are often paired with creatine to support muscle recovery and growth. Additionally, branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and beta-alanine are commonly used in conjunction with creatine to optimize performance and reduce muscle fatigue.
Effectiveness and potential risks
While combining creatine with other supplements can be beneficial, it is essential to understand the potential risks and interactions. Some supplements may have similar effects or mechanisms of action, which could lead to overstimulation or unwanted side effects. Before combining creatine with other supplements, consult with a healthcare professional to ensure compatibility and safety.
Consulting with a healthcare professional
If you are unsure about which supplements to take or how to combine them with creatine, it is always recommended to seek guidance from a healthcare professional. They can provide you with personalized advice based on your specific needs, goals, and health status. Consulting with a professional will help ensure that you are making informed decisions and taking supplements safely.

Monitoring and Tracking Progress
Setting goals and expectations
When taking creatine, it is essential to set realistic goals and expectations. Creatine is not a magical solution that will transform your physique overnight. Instead, it should be viewed as a tool to support your training and assist in achieving your desired outcomes. Set measurable goals, such as increasing your strength or improving your athletic performance, and track your progress accordingly.
Measuring progress and performance
To accurately measure your progress, it is beneficial to track various factors such as your strength gains, muscle measurements, and individual performance metrics. Keep a record of your workouts, including the weights lifted, sets, and repetitions performed. By consistently monitoring these variables, you can determine if creatine supplementation is positively impacting your progress.
Adjusting dosage if necessary
Every individual’s response to creatine may vary. If you do not experience the desired results or notice any adverse effects, you may consider adjusting your creatine dosage or exploring alternative forms of creatine. It is essential to listen to your body and make adjustments based on your individual needs and preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can women take creatine?
Yes, women can safely take creatine. While most studies on creatine supplementation have been conducted on men, there is growing evidence suggesting that women can also benefit from its use. Creatine supplementation can help women improve their strength, increase muscle mass, and enhance sports performance. However, as with any dietary supplement, it is best to consult a healthcare professional before beginning creatine supplementation.
Does creatine cause weight gain?
Although creatine can cause a slight increase in body weight due to water retention within the muscles, it does not directly cause fat gain. Any weight gain associated with creatine supplementation is typically temporary and may subside once the supplementation is discontinued. Creatine primarily helps with strength and muscle gains rather than promoting overall weight gain.
Is creatine safe for teenagers?
As with any supplement, it is essential for teenagers to approach creatine supplementation with caution. The long-term effects of creatine supplementation on developing bodies are not yet fully understood. Therefore, it is recommended that teenagers avoid creatine supplementation unless under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Creatine is a popular and effective supplement for individuals looking to improve their strength, increase muscle mass, and enhance their athletic performance. When taken correctly, creatine can provide numerous benefits without significant side effects.
However, it is essential to consider individual factors, closely monitor progress, and consult with healthcare professionals to ensure safe and optimal use of creatine. With proper guidance and research, creatine can be a valuable addition to your fitness regimen. Start your creatine journey today and unlock your full potential.




